Whitepaper
Travel Tit-For-Tat: Travel Trends in Malaysia
Learn how the Malaysian tourism and hospitality sectors are faring since COVID-19. Get the latest facts and travel trends.
According to the National COVID-19 Immunisation Programme Coordinating Minister Khairy Jamaluddin, the government has secured enough COVID-19 vaccines to cover 130% of the entire country’s population.
As of August 2021, seven brands of COVID-19 vaccine have been approved for use in Malaysia.
This whitepaper aims to understand Malaysia’s sentiment towards the National COVID-19 Immunisation Programme on social media platforms and news sites.
We’ve delved into the sentiment surrounding the Malaysian National COVID-19 Immunisation Program across social media and traditional news coverage. Learn what the Malaysian population feels about the program and related topics in our latest whitepaper.
Download the whitepaper and read more.
Loren is an experienced marketing professional who translates data and insights using Isentia solutions into trends and research, bringing clients closer to the benefits of audience intelligence. Loren thrives on introducing the groundbreaking ways in which data and insights can help a brand or organisation, enabling them to exceed their strategic objectives and goals.
Non-favourable travel trends in Malaysia have emerged due to the tourism and hospitality sector losing over 80% of its business since March 2020. The Government has imposed strict movement control orders curbing rapidly increasing COVID-19 cases.
Since March 2020, Malaysia’s tourism and hospitality sector has lost over 80% of its business due to strict movement control orders imposed to curb the rapidly increasing COVID-19 cases.
Domestic travel was allowed from June to September last year as Malaysia eased lockdowns nationwide. However, this did little to help the flailing tourism industry.
Apart from regular promotions and offers, some businesses in the travel and F&B industries have sought creative ways to keep their brands at the top of their minds and keep them interested in their respective sectors.
Download the whitepaper and read more.
" ["post_title"]=> string(45) "Travel Tit-For-Tat: Travel Trends in Malaysia" ["post_excerpt"]=> string(122) "Learn how the Malaysian tourism and hospitality sectors are faring since COVID-19. Get the latest facts and travel trends." ["post_status"]=> string(7) "publish" ["comment_status"]=> string(4) "open" ["ping_status"]=> string(4) "open" ["post_password"]=> string(0) "" ["post_name"]=> string(25) "travel-trends-in-malaysia" ["to_ping"]=> string(0) "" ["pinged"]=> string(0) "" ["post_modified"]=> string(19) "2023-07-07 03:20:01" ["post_modified_gmt"]=> string(19) "2023-07-07 03:20:01" ["post_content_filtered"]=> string(0) "" ["post_parent"]=> int(0) ["guid"]=> string(32) "https://www.isentia.com/?p=16318" ["menu_order"]=> int(0) ["post_type"]=> string(4) "post" ["post_mime_type"]=> string(0) "" ["comment_count"]=> string(1) "0" ["filter"]=> string(3) "raw" }Learn how the Malaysian tourism and hospitality sectors are faring since COVID-19. Get the latest facts and travel trends.
Telekung Siti Khadijah (TSK), engaged Isentia to help them better understand their audience, stand out from counterfeit products, communicate their brand value and differentiate themselves from competition from both established and counterfeit players.
As communications professionals look toward 2026 planning sessions, one question dominates the conversation - How can we use AI in a safe, scalable, and sustainable way?
Behind this question often lies the hope for an "AI easy button"—a one-click solution for complex measurement challenges. However, as discussed in our recent APAC webinar, the real opportunity lies not in automating old metrics, but in architecting a smarter era of measurement.
Hosted by Russ Horell, Isentia’s Chief Revenue Officer for APAC, the session featured deep dives from two industry leaders who've contributed immensely to research and planning: Ngaire Crawford (Director of Insights, ANZ) and Prashant Saxena (VP of Research and Insights, SEA). Together, they unpacked the transition from using insights and converting them into strategic, measurable storytelling.
Here are the key takeaways from the discussion.
If 2024 and 2025 were the years of "playing in the sandbox," 2026 is set to be the year of transparency.
Ngaire Crawford emphasized that while AI is incredible at summarising data and recognising patterns, it does not automatically generate insight. As we integrate these tools, the focus must shift to methodological integrity—understanding the source data, the structure, and the limitations of the models we use.
"Models are really good pattern finders. But they don't necessarily set what good looks like, or understand the consequences of being wrong. And the antidote to that is always going to be good design." – Ngaire Crawford
A major misconception remains that feeding AI endless amounts of data will naturally result in better answers. In reality, without the right framework, more data often just creates more noise.
Prashant Saxena warns against the "sameness" that AI can generate. If everyone uses the same models on the same big data sets without specific objectives, they will get similar, generic answers. The role of the insights professional is evolving from descriptive reporting to strategic storytelling—using judgment to break through the "echo chamber" of AI validation.
The panelists played a game of "keep, kill, create" to determine the future of measurement metrics.
"Authenticity is more upstream, as reputation and trust are more downstream... That's an authentic ritual on a day-to-day basis, which leads to reputation." – Prashant Saxena
Despite the technical buzz surrounding AI, the panel argued that communications professionals hold a distinct advantage. "Prompt engineering" is, at its core, a language and communication skill.
The future doesn't necessarily belong to the most technical users, but to the most articulate—those who can clearly define an outcome, ask the right questions, and deconstruct language to get the best result from a model.
As we move into 2026, the advice from our experts is to not let AI replace your strategic point of view.
By combining the speed of AI with the nuance of human strategy, communicators can finally build the sophisticated measurement systems they have always wanted.
Interested in viewing the whole recording? Watch our webinar here.
Alternatively, contact our team to learn more insights into meaningful measurement, KPIs and communicating using the right dataset.
Our recent webinar explores what the future of measurement in 2026 looks like and what brands must do to scale in this AI era.
The media landscape is accelerating. In an era where influence is ephemeral and every angle demands instant comprehension, PR and communications professionals require more than generic technology—they need intelligence engineered for their specific challenges.
Isentia is proud to introduce Lumina, a groundbreaking suite of intelligent AI tools. Lumina has been trained from the ground up on the complex workflows and realities of modern communications and public affairs. It is explicitly designed to shift professionals from passive media monitoring back into the role of strategic leaders and pacesetters.

“The PR, Comms and Public Affairs sectors have been experimenting with AI, but most tools have not been built with their real challenges in mind.” said Joanna Arnold, CEO of Pulsar Group.
“Lumina is different; it is the first intelligence suite designed around how narratives actually form today, combining human credibility signals with machine-level analysis. It helps teams understand how stories evolve, filter out noise and respond with context and confidence to crises and opportunities.”
Lumina is centered on empowering, not replacing, the human element of communications strategy. This suite is purpose-built to help PR, Comms, and Public Affairs professionals significantly improve productivity, enhance message clarity, and facilitate early risk detection.
Lumina enables communicators to:
We are launching the Lumina suite by making our first module immediately available: Stories & Perspectives.
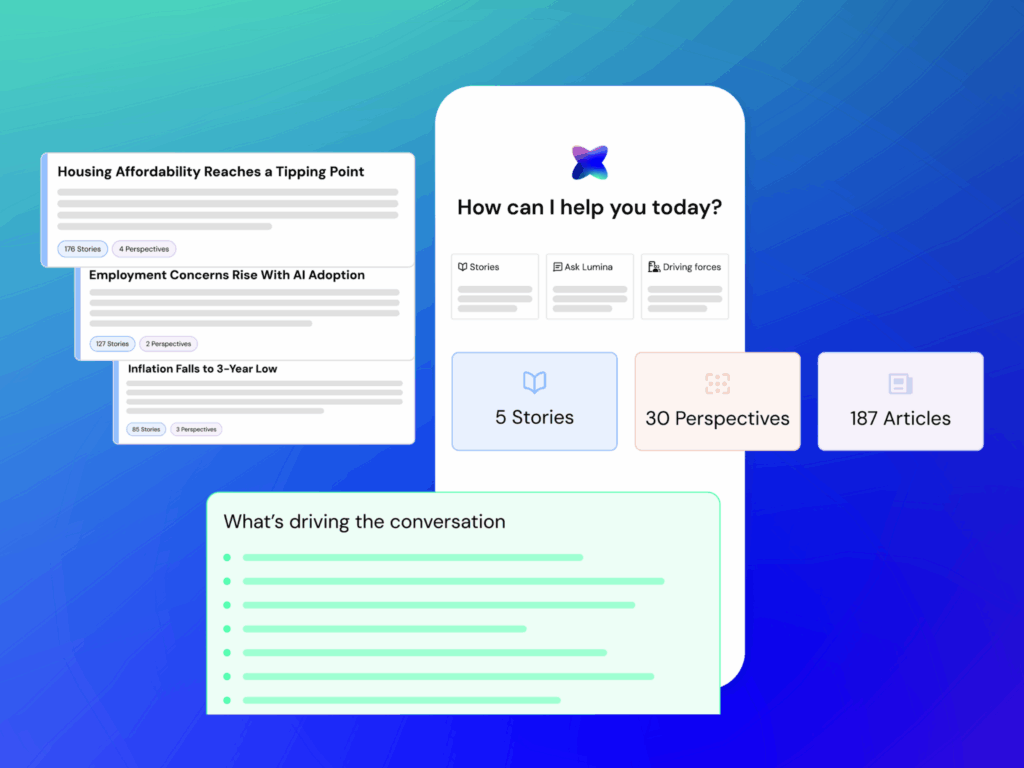
In the current fragmented, multi-channel media environment, communications professionals need to be able to instantly perceive not just how a story is growing, but also how it is being perceived across different stakeholder groups.
Stories & Perspectives organizes raw media mentions into clustered, cohesive Stories, and the Perspectives that exist within each, reflecting distinct media, audience, and public affairs angles. This unique functionality allows users to:
"Media isn’t a stream of mentions," said Kyle Lindsay, Head of Product at Pulsar Group. "But rather a living system of stories shaped by competing perspectives. When you can see those structures clearly, you gain the ability to understand issues as they form, anticipate how they’ll evolve, and act with precision. That’s what we mean when we talk about AI built for communicators, and that's what an off-the-shelf LLM can't give you."
The launch of Stories & Perspectives is the first release of many. Over the upcoming months, we will systematically roll out the full Lumina roadmap, introducing a comprehensive set of AI tools engineered to handle every phase of the communications lifecycle.
The full Lumina suite will soon incorporate:
Want to harness the power of Lumina AI for your PR, Comms, or Public Affairs team? .
Complete the form below to register your interest.
Get in touch or request a demo.