Blog
Analysing Australia’s higher education landscape in 2025
A deep dive into how global audiences perceive Australian higher education and the university sector with a spotlight on the SEA region.
“In the future there will be no female leaders, there will just be leaders”
— Sheryl Sandberg
Our recent partnered research with Women in Media showed there is still significant gender discrimination within the media and a long way to go before parity is reached. Female voices are being excluded in shaping public perception in industries where women lead in employment, such as retail, sport and health. This creates hurdles for female experts and sources, and demonstrates the largest gap between women employment share and media representation.
All organisations have a role to play, with a responsibility to provide equal opportunities and outcomes for men and women.
Through the power of collaboration and raising each other up, it presents an opportunity for women to change the status quo.
Women’s voices and women’s participation within the workplace are lacking true representation and the amplification they deserve. Whether it’s in leadership, as a spokesperson or across the news value chain – there’s more that can be done to avoid misrepresentation of an organisation as this sends a conflicting message to their audience.
As the Women in Media research suggests, to avoid underrepresentation, organisations should:
Workplaces have a responsibility to ensure there is a focus on gender balance through inclusion and diversity as well as provide support and visibility of pathways to leadership roles.
When choosing a spokesperson, it’s the role of an organisation to select someone who is a well suited representative, and be able to provide the best answers for their key audiences. The characteristics of a spokesperson are similar to that of a leader, with competency (37%), confidence (31%), and good communication (26%) being the most important. They also need to speak with authority, with their opinions being trusted, but also an ability to connect with stakeholders and not shy away from empathy, if it’s needed.
Women need to be given the support and authority to be a trusted brand ambassador or spokesperson for the organisation.
At a time when a story hits the media, there is a framework organisations can put into place to ensure success:
The Women in Media Scorecard explores the visibility of women as authors, participants and subjects of news in Australian media. It identifies core areas in media analytics (bylines, sources, experts) to monitor change over time and positive or negative shifts towards achieving parity for women in Australian media. Isentia analysis included 18,346 reports from Australian press, radio and TV news coverage over a 14-day period, from 18-31 July 2022.

Some say a woman alone has power; collectively they have impact.
Across all industries and organisations, when it comes to women supporting other women, there is power in the pack.
Women often underestimate the value they can offer, the wisdom and knowledge they can share can benefit and support many women (and men too).
From increasing productivity and enhancing collaboration, to inspiring organisational dedication and boosting confidence, women can be unstoppable when working towards a desired goal, together.
“Women need to get behind other women. Encourage their expertise. Acknowledge their strengths. Champion their success. Amplify their voice.”
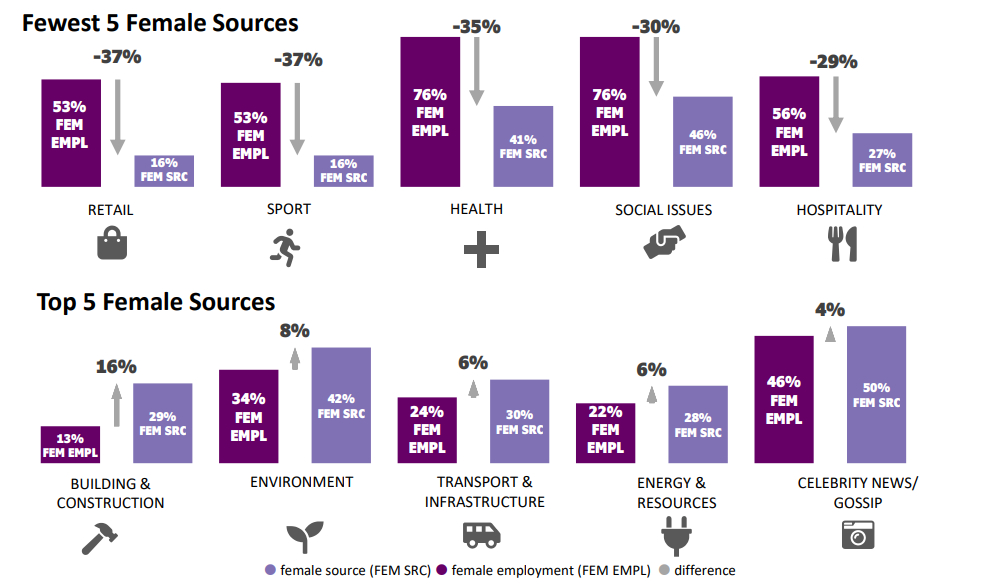
Interestingly, our research shows female reporters are 30% more likely to quote female sources than male reporters. This suggests that women do support women, yet women dominated industries are not being represented as such in the media. The highest underrepresentation of female sources tended to be associated with topics/sectors with a high female employment share, for example in retail, sport and health.
This presents an opportunity for organisations to increase women’s representation in leadership positions and boost women’s workforce participation. By doing this, it will encourage women to amplify other women and contribute to achieving gender parity within the workplace.
Source gender split vs industry employment
The media hype plus cultural perceptions might showcase that women don’t want to revel in another woman’s success. Yet it’s quite the opposite.
Dedicated days like International Women’s Day are a great opportunity to celebrate the achievements of other women beyond the divisions of national, ethnic, cultural, economic or political barriers. But it shouldn’t stop there.
Status quo bias and gender blindness are two key areas of bias within organisations. For whatever reason, when we think about a leader or a person with authority, our brains default to think of a male. The ‘think manager, think male’ norms continue to hold women back and contribute to a notable gender gap in self promotion within the workplace.
Women are 33% less likely to promote their performance and only 60% of women actively make people aware of their accomplishments. And this wasn’t due to a lack of desire, however it was more likely to attribute their failures to lack of ability. Because women feel the workplace is harder on them, they’re harder on themselves, causing their confidence to take a hit. Yet for women to advance in leadership roles or further their career, self-promotion is a must.
In instances where women are confident and assertive at work, they can be penalised by others and be referred to as bossy. In fact, women are twice as likely to be branded as bossy in the workplace for doing the same behaviours as men.This can often impact their desire to celebrate their achievements and also have a negative impact on how well they are liked by their peers.
Within the media landscape in particular, women reporters are more likely to:
Yet they don’t get seen as experts in their field and get the bylines to showcase this.
The Women in Media research shows only two of the 35 identified topic groups (6%) recorded a greater share of women sources than men. Females are notably under-represented when comparing the share of experts in media reporting with the share of sector employment. The pattern of media underrepresentation in women-dominated industries extends from sources to the share of experts quoted.
With the spotlight on gender equity, now is the time for women to support and amplify other women across all industries.
At Isentia equity, inclusion and diversity is something we are all passionate about and we choose partnerships that help us shine a light on these issues. We value the voice that our women leaders and employees can have within our company and industry and are always looking for opportunities to elevate their voices.
Company CEO Joanna Arnold believes ‘the true value of insights is when it’s used to shine a light on societal issues and inspire behaviour that drives change. Our innovation in audience intelligence underpins our purpose to help surface the diverse voices shaping wider societal narratives’ so that they can be better represented in the media and other channels shaping public perception”.
The Women in Media Research highlights that much work remains to provide gender equity and share of voice for women in organisations and through representation in Australian media.
Organisations can play an important role in gender equity by:
Moving forward, as more women encourage and support other women, the more will be received in return.
We can continue to support the positive impact organisations have towards female representation and gender parity. We want to improve the barriers and drivers for women representation in organisations across societal, organisational and individual levels.
If you’d like to learn more about The Women in Media Scorecard or discover how Isentia can help your organisation with impactful insights-driven research, get in touch with us today.
References
Women in Media Report, 2022
Isentia’s Leadership Index 3: Leading Through Change
https://www.ccl.org/articles/leading-effectively-articles/bossy-whats-gender-got-to-do-with-it/
https://hbr.org/2019/12/why-dont-women-self-promote-as-much-as-men
Loren is an experienced marketing professional who translates data and insights using Isentia solutions into trends and research, bringing clients closer to the benefits of audience intelligence. Loren thrives on introducing the groundbreaking ways in which data and insights can help a brand or organisation, enabling them to exceed their strategic objectives and goals.
Get in touch or request a demo.