Blog
The fundamentals of stakeholder strategy
A practical guide to tailored stakeholder management, offering strategies and tools to identify, map, and nurture relationships.
You’ve probably heard of REDcycle by now – the initiative started by a passionate mum, providing Australian’s with the opportunity to recycle their soft plastics. Its operation helped reduce the amount of landfill in Australia and its sudden halt in operation sent the community into a frenzy.
The pause in the popular REDcycle program presented an opportunity to rethink the model for soft plastics recycling in Australia and find end markets for recycled package content. It also prompted Australians to rethink the way they consume products, rather than just the way they recycle them.
Social media conversations show Australians continue to encourage retailers and large corporations to use their influential power to create impactful change. These conversations are heightened where regression (or progression) is made towards sustainability.
As Australians become more conscience about their soft plastic usage, it raises the question of whether the collapse of the REDcycle program was a blessing in disguise or more of a curse on sustainability?
From the end of October 2022 to the end of March 2023, Australians have consistently felt negative sentiment towards REDcycle’s collapse with spikes when key announcements were made by the organisation. Overall, close to 45% of Aussies felt negatively compared to 18.5% positive.

As people learned the news about REDcycle, there was heightened concern about how soft plastics were going to be recycled. With over 12,000 mainstream media items about REDcycle or soft plastic recycling, it supports the idea that Australia’s broken plastic recycling system is distressing for many and more needs to be done.
The halt in operation brought on more concern for the environment and ignited feelings of anger and distrust after thousands of tonnes of plastic had been stockpiled instead of being recycled.
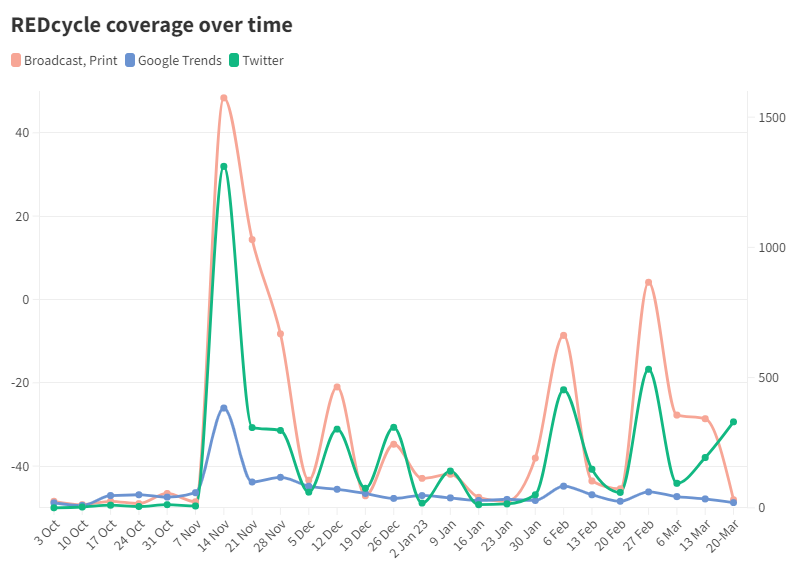
Media coverage across different channels (social media, search, broadcast and print) shows spikes of coverage on the same days (9 November, 7 February, 27 February) but at varying levels;
Conversations on Twitter represent social media as the preferred option for users in comparison to broadcast, print and search.
As political leaders have the power to influence their supporters on sustainability development, sustainability advocates are pushing Australian leaders to accelerate plastic waste regulations.
Conversations on Reddit rapidly grew on 9 November – the day the REDcycle program paused. Overall sentiment was anger and sadness with many expressing their feelings of disappointment after learning their donated soft plastics were not ending up where promised. Others felt frustrated or angry towards large organisations who were not holding up their end of the deal, especially after taking the time to correctly separate their recyclable waste.
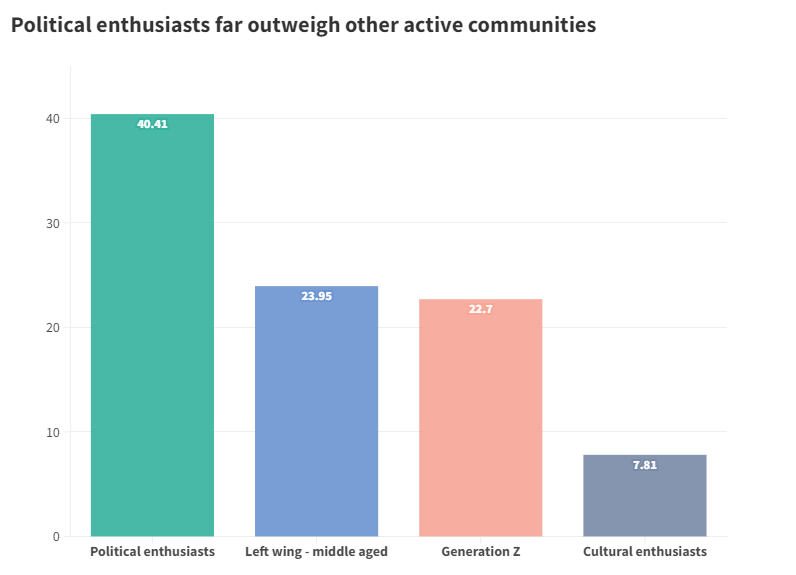
At 40%, political enthusiasts far outweigh any other active community on social media and forums. Their ‘passion’ for Australia can be overshadowed, as they share their beliefs towards the government – ranging from incompetence to over governing. Generation Z are true digital natives and make up 22% of active online communities. This cohort is motivated to make more sustainable choices, if it means it will benefit the environment for the long term.
The REDcycle program illustrated the complexity of soft plastics recycling and the need to build robust systems to close the loop on this common household waste. For years there have been stockpiling issues, dumping, toxic fires and lax regulations, making it challenging to operate.
Australia’s largest supermarkets continue to work towards reducing unnecessary plastics in their stores, and support the development of circular economies through the use of recycled material.
Supermarket chains have moved quickly to find an alternative solution, teaming up with the National Plastics Recycling Scheme (NPRS) with financing from the Federal Government and top food and grocery producers to establish the Roadmap to Restart Taskforce.
23 February 2023, supermarket giants announced the return of soft plastics recycling by late 2023, despite the lack of recyclers. This announcement generated 6 x the amount of ‘supermarket’ Twitter mentions compared to 1 Nov 2022.
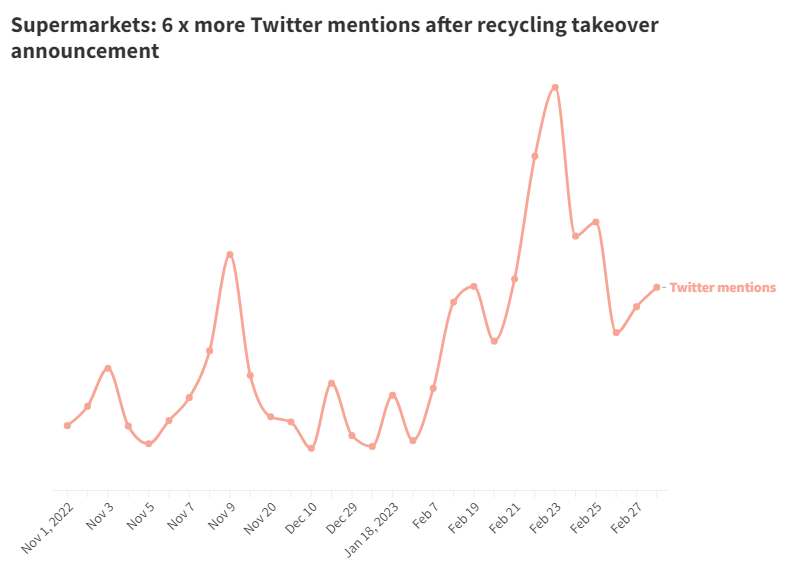
Although it’s a promising development, announcements like these are what drive the conversations and force change. This rings true as sustainability advocates push for more substantial action to address soft plastic waste in Australia.
Large organisations are being challenged to rethink how they package their products and how they can be more sustainable, what about the government?
Minister for Environment and Water, Tanya Plibersek, has been vocal in her response to the soft plastics recycling crisis. Initially, the program’s failure was met with calls for urgent action with Ms Plibersek weighing in on the news, saying it was “really concerning” and put the pressure on major supermarkets to come up with an alternative recycling program.
Although it is acknowledged that the government plays a role, it has been made clear the responsibility also lies with manufacturers and packagers.
State and Federal Ministers are actively sharing their opinions and policies online in an effort to make change faster and positively influence their audience. Victorian Premier, Dan Andrews and the Victorian Government are leading the way, banning the selling and supply of single-use plastics in the state.
Commonwealth, State and Territory governments have jointly invested considerable funds into developing local capabilities to recover the challenging recycling stream and have committed to turning around Australia’s lack of progress on its recycling targets, setting new targets for 2025.
Adding another interesting layer of insights on social media from our sister company Pulsar, is that reddit is playing a major role in disseminating sentiment surrounding the REDcycle program. The below chart shows the most recurring keywords grouped by channel. The larger the tile, the more times the topic has appeared in that channel. Conversations involving scientists were notable and finding a solution to plastic pollution was a key narrative.
Trust was also a recurring keyword across all channels, indicating trust needs to be rebuilt. is something that needs to be rebuilt. Australians have begun to lose faith in the recycling industry as there is a lack of transparency into how much actually gets recycled.
The introduction of a new taskforce – the Road to Restart – will work towards rebuilding the public trust in soft plastic recycling. The taskforce also endeavours to ensure supermarkets and the packaging sector will get it right on their own accord.
Conversations through online forums show Australians deeply care about sustainability, stating that ‘unless it can be recycled, it shouldn’t be produced.’
Social media platforms are especially fueled by sustainability advocates who need to share a broader awareness of recycling initiatives and earn potential audiences – conversations are widespread and emotions are elevated. Whereas broadcast and print channels are sharing the facts and the need to know information, directing audiences to use the information they have and to search where they can take their soft plastics. In addition to sustainability advocates, everyday Australians are learning how to pivot, seeking out support and ideas from fellow supporters on Twitter and other social media platforms.
If organisations can work together and policymakers can set clear legislative frameworks, it’s possible to implement necessary changes in both manufacturer and consumer behaviour to create a thriving circular plastics economy.
The pause of REDcycle is certainly on its way to being a good thing for the environment.
If you would like to learn more about discovering how media intelligence can lead to insights across environmental issues or the active communities leading the conversations using audience intelligence, get in touch with us today.
Loren is an experienced marketing professional who translates data and insights using Isentia solutions into trends and research, bringing clients closer to the benefits of audience intelligence. Loren thrives on introducing the groundbreaking ways in which data and insights can help a brand or organisation, enabling them to exceed their strategic objectives and goals.
A practical guide to tailored stakeholder management, offering strategies and tools to identify, map, and nurture relationships.
Across the communications landscape, teams are being asked to do more with less, while staying aligned, responsive and compliant in the face of complex and often shifting stakeholder demands. In that environment, how we track, report and manage our relationships really matters. In too many organisations, relationship management is still built around tools designed for […]
Get in touch or request a demo.