Blog
Analysing Australia’s higher education landscape in 2025
A deep dive into how global audiences perceive Australian higher education and the university sector with a spotlight on the SEA region.
Australia’s upcoming social media ban for minors hasn’t been primarily driven organic debate. Instead, it’s unfolded through a deliberate, tightly paced sequence of government-led communications, each phase designed to build momentum, secure legitimacy, and keep control of the public narrative.
What we’re seeing in the media data isn’t a spontaneous rise in interest, but a pattern of spikes that line up neatly with major government moments. Each one serves a purpose in a broader narrative strategy, and each reveals something about where the public conversation is heading next.

The rollout of Australia’s social media ban has followed something of a three-act script. It really began on the world stage, with Prime Minister Albanese’s UN address framing the policy as a “world-first” and earning global praise that positioned Australia as a leader rather than a legislator under pressure, a narrative heavily amplified across bulletins nationwide. Momentum built when Denmark echoed the proposal, turning the story from an Australian policy into a global movement and giving journalists a reason to return to it without new domestic detail. Subsequently, the focus shifted home, with the launch of the government’s ad campaign. Coverage has moved from delivery to confirmation, from diplomacy to daily life, embedding the message of child safety through stories designed to connect emotionally with parents before the ban takes effect.
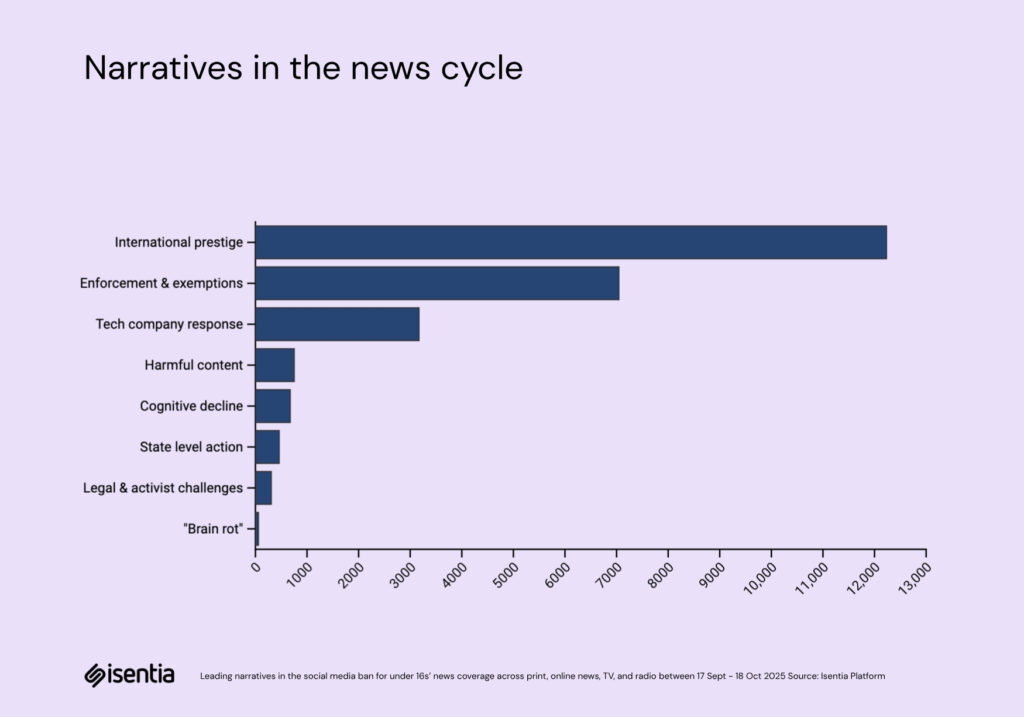
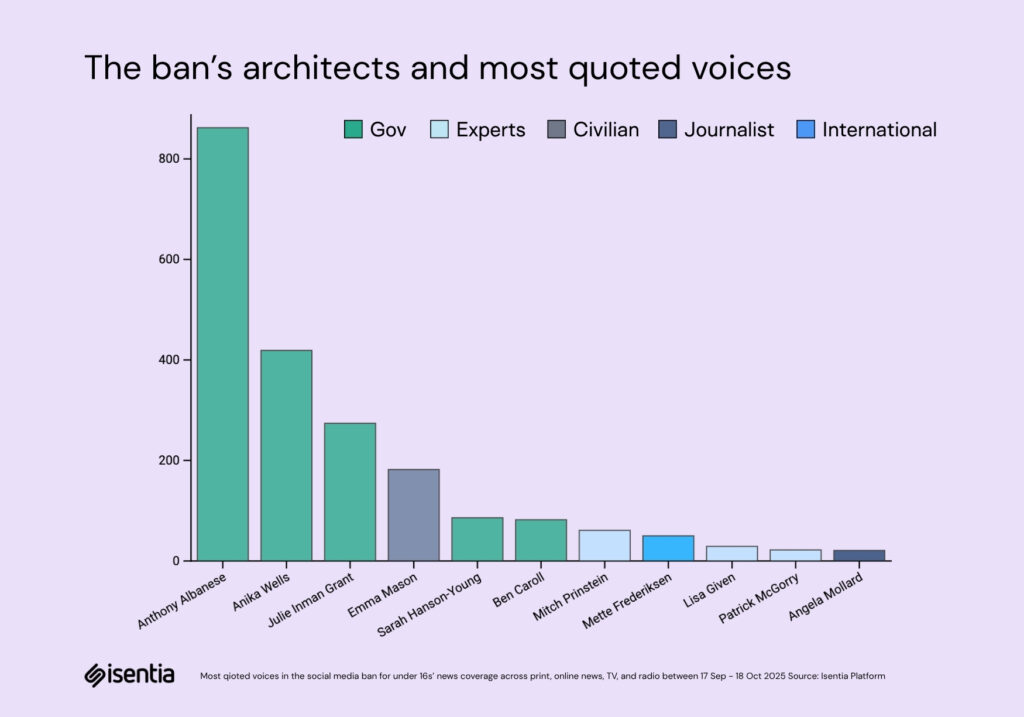
Media coverage of the social media ban is being driven by a hierarchy of voices. At the top are the political architects, Anthony Albanese and Anika Wells, who account for 68% of all quoted commentary. Their dominance reflects a message tightly controlled from the centre, with each public appearance designed to reinforce authority and focus the debate. eSafety Commissioner Julie Inman Grant follows as the enforcer, providing regulatory credibility and keeping the story alive through ongoing updates and meetings with tech companies.Around them, Emma Mason’s personal story gives the policy its emotional weight, while expert voices like Dr Jason Nagata and Mitch Prinstein lend scientific legitimacy. Counter-voices such as Patrick McGorry are present but faint, just 1% of total commentary. Together, these strands create a coordinated ecosystem where political leadership, regulation, expertise, and emotion work in unison to sustain a single, dominant narrative.
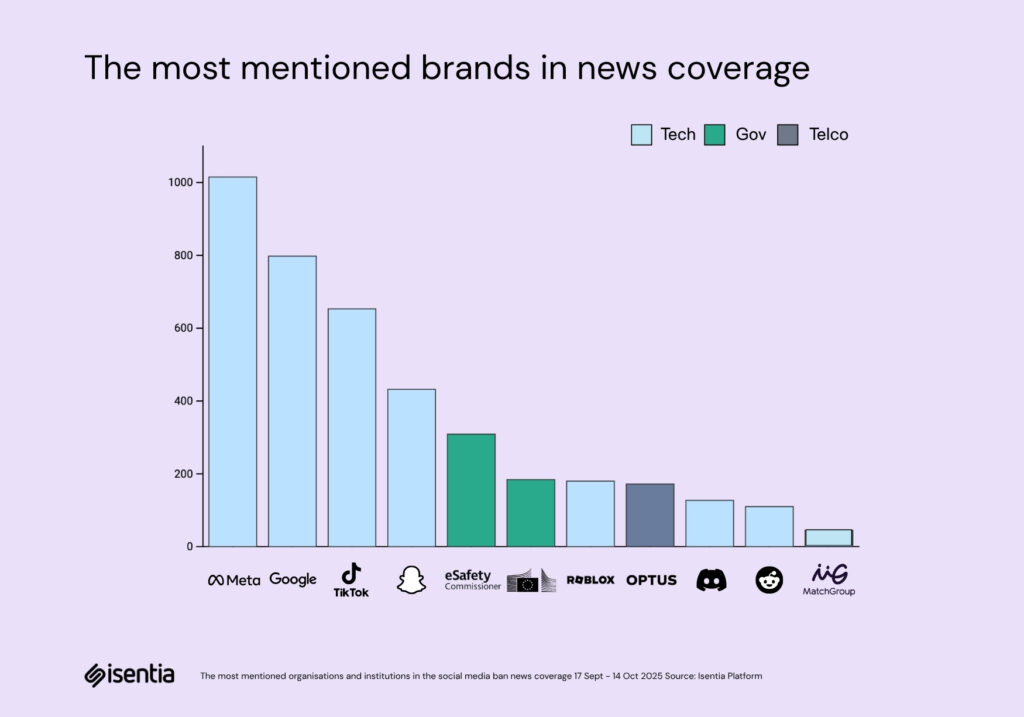
The next layer of coverage reveals how the story’s momentum is being sustained, not just by government messaging, but by the constellation of organisations caught in its orbit. Meta, Google, TikTok, and Snapchat remain the gravitational centre of the conversation, collectively shaping more than a thousand mentions each. They are the policy’s focal point and the media’s shorthand for what’s at stake.
Stories about ministerial meetings, enforcement challenges, and pleas for exemptions ensure these brands stay in the headlines, but on government terms, framed as subjects of regulation rather than equal participants in debate. This has also surfaced one of the key underlying questions: Will the ban actually work? There is a significant narrative thread focused on the practical challenges of enforcement, with YouTube widely quoted in the media as saying the ban is “‘extremely difficult’ to enforce”.
With the media also reporting that the government will rely on “artificial intelligence (AI) and behavioural data to reliably infer age” rather than hard age verification, the public is left asking: If tech giants say it’s unenforceable and teens are already finding ways around it, what will this law actually achieve?
The eSafety Commission anchors the enforcement narrative, while the European Commission’s support sustains the “world-first” framing abroad. As the scope of the ban widens, platforms like Roblox, Discord and Reddit have been pulled into focus, signalling how the policy, and its coverage, keeps expanding. This has forced the core question into the open: What is a “social media platform” in 2025?
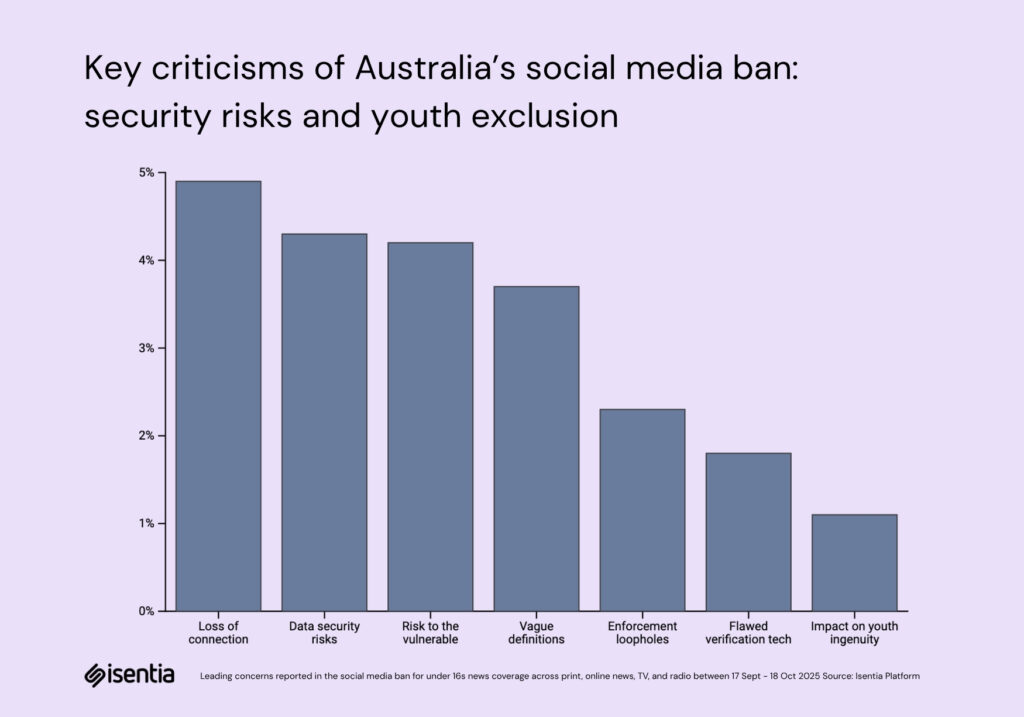
Although the government’s narrative still dominates, a set of counter-stories is emerging, focusing on the policy’s real-world consequences. Central to these stories are concerns about young people losing access to vital online connections, particularly among regional or marginalised communities. Advocates for the LGBTIQA+ community and youth mental health experts like Professor Pat McGorry argue that the ban could isolate teenagers who rely on online spaces for support, and entrepreneurial opportunities. Other reporting has questioned the reliability of AI-based age verification, the volume of data collected, and the risk that well-intended rules might backfire, creating unintended consequences that contradict the policy’s goal of child safety. These counter-narratives remain smaller in scale than the dominant political messaging, but they cut through because they frame the debate around everyday impacts rather than top-down authority.

A particularly visible strand of coverage centres on the unclear definition of “social media” in the legislation. While the public typically thinks of platforms like Instagram and TikTok, the law’s wording has forced a broader debate that draws in platforms such as Roblox, Discord, and Steam. The eSafety Commissioner’s proactive enforcement measures have highlighted these regulatory ambiguities, prompting media to question whether platforms with different primary purposes should be included and whether the policy might trade one harm for another. Discord drew attention following a poorly timed data breach, which the public and media linked to potential ID theft risks. These reports show how regulators and secondary players can keep the conversation alive, highlighting risks, opening new angles, and forming alliances that complicate the policy debate. A notable example is YouTube’s effort to argue it should not be classified as a social media platform, citing the platform’s role in launching careers like Australian artist Troye Sivan as part of a broader cultural and creative ecosystem.
Together, these stories illustrate that while the government controls the main narrative, emerging counter-voices are beginning to shape the media conversation in ways that emphasise practical and social realities.
Loren is an experienced marketing professional who translates data and insights using Isentia solutions into trends and research, bringing clients closer to the benefits of audience intelligence. Loren thrives on introducing the groundbreaking ways in which data and insights can help a brand or organisation, enabling them to exceed their strategic objectives and goals.
Get in touch or request a demo.