Blog
Analysing Australia’s higher education landscape in 2025
A deep dive into how global audiences perceive Australian higher education and the university sector with a spotlight on the SEA region.
The biggest influence on public perception of the 2025 election campaign was not policy. It was identity, culture wars, and a growing fear of Australia ‘becoming America’. What began as a focus on easing the cost of living quickly widened into a broader debate about national identity. Media coverage and social media feeds revealed a tug of war. On one side was policy messaging. On the other, gaining considerable ground, were culture and identity narratives fuelled by anxiety over external influence.
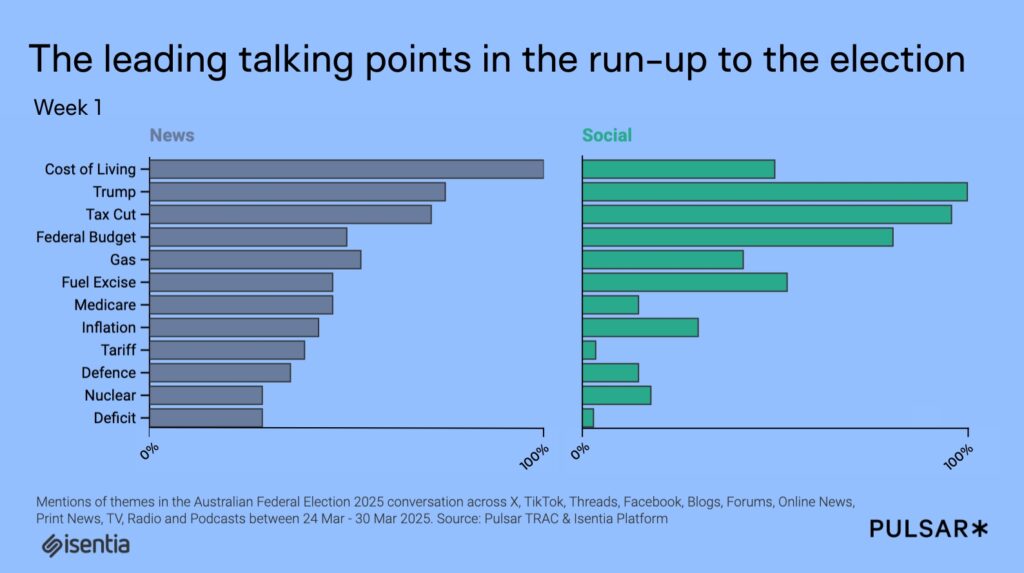
At the start of the election cycle in early March, news coverage centred on cost of living pressures and tax cuts. The Labor government’s budget announcement and the Liberal Party’s response cemented the agenda, with topics like supermarket price gouging, fuel excises, and nuclear energy proposals striking a chord with voters. Early discussion on social media showed a clear focus on making life more affordable for families. But in the background, frustration around Donald Trump’s proposed tariffs and concerns about Australia–U.S. relations began to surface. Peter Dutton’s early promise to cut 40,000 public service jobs and push for a return to office work further fuelled comparisons between Dutton and Trump among Australian audiences.
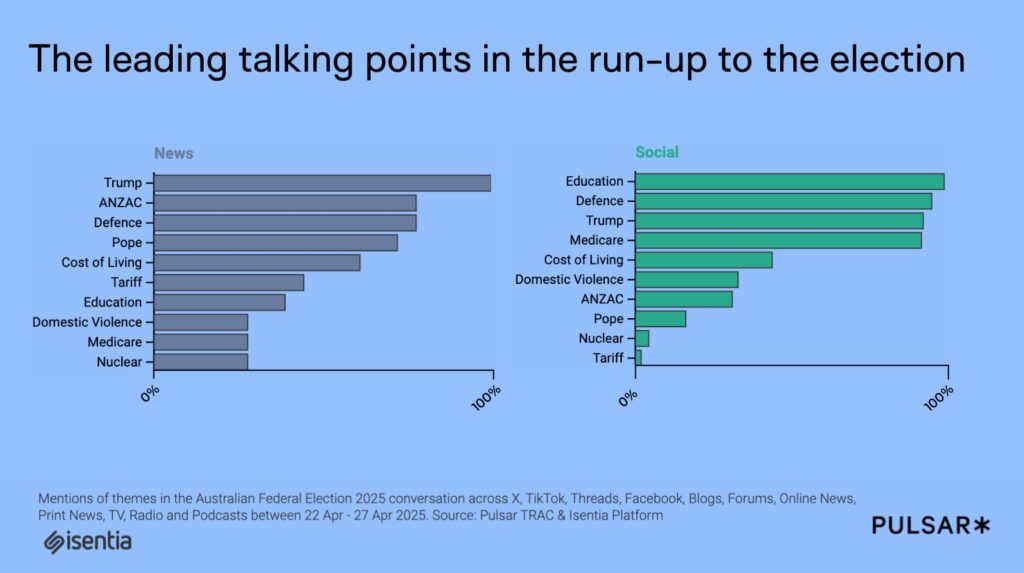
As the election cycle progressed, international events and conflicts moved to the forefront. Trump’s presence in global headlines alongside Canada’s similarly timed election, intensified comparisons between Australian and Canadian public attitudes toward American influence. Media narratives shifted from domestic cost-of-living concerns to broader conversations about defending the Australian way of life and protecting national interests particularly in education, reshaping the battleground on which voters made their decisions.

On March 28, coverage and discussion spiked as Anthony Albanese officially announced the election date. Earlier, on March 10, a surge in conversation centred on new polling that suggested a potential hung parliament, sharpening media focus on Labor. Albanese’s appearance on Today, where he responded to frustrations about delayed campaigning with, “We’re just about helping people, because that’s what people expect,” reinforced his image as a community-focused leader and contrasted with how past prime ministers were criticised during disasters. Meanwhile, Peter Dutton’s social media attention rose on April 12, as reports surfaced of his opponent Ali France leading in Dickson while a local tent encampment was demolished by Moreton Bay Council. Dutton, campaigning in Perth during the demolition, attracted criticism. A few days later, a compilation of clips linking Dutton to Donald Trump circulated widely. These moments highlighted the distinct leadership styles that shaped voter perceptions throughout the campaign.
Although Labor drew the most attention overall, Dutton and the Liberals gained momentum across social media. The Liberal Party’s early use of trends, AI tools, and memes attracted conversation, but the involvement of influencers and podcasts proved polarising. Coverage also highlighted a generational divide, with young women leaning left and young men leaning right. Influencers played a key role in shaping these dynamics, from Albanese’s Happy Hour podcast appearance on March 26, where his “delulu with no solulu” challenge dominated news cycles, to Dutton’s interview on Sam Fricker’s podcast aimed at young male voters. As the campaign progressed, news increasingly focused on character attacks and gaffes at the expense of policy debate. Issues like housing, supermarket competition, HECS relief, and energy bills remained core to party platforms, but many audiences were drawn into yarns covering personality clashes and culture wars.

The most shared news items from the beginning of the campaign to recently underline this shift of attention to cultural conflict. Posts about the mobilisation of Muslim voters around Gaza, criticism of Liberal candidates campaigning in military uniforms, warnings about public service job cuts, and debates over the political leanings of young male voters all reveal how specific cultural flashpoints and niche group appeals dominated discussion. Instead of broad policy debates, election discourse was fragmented into controversies that inflamed identity-driven tensions, polarised audiences, and heightened distrust.
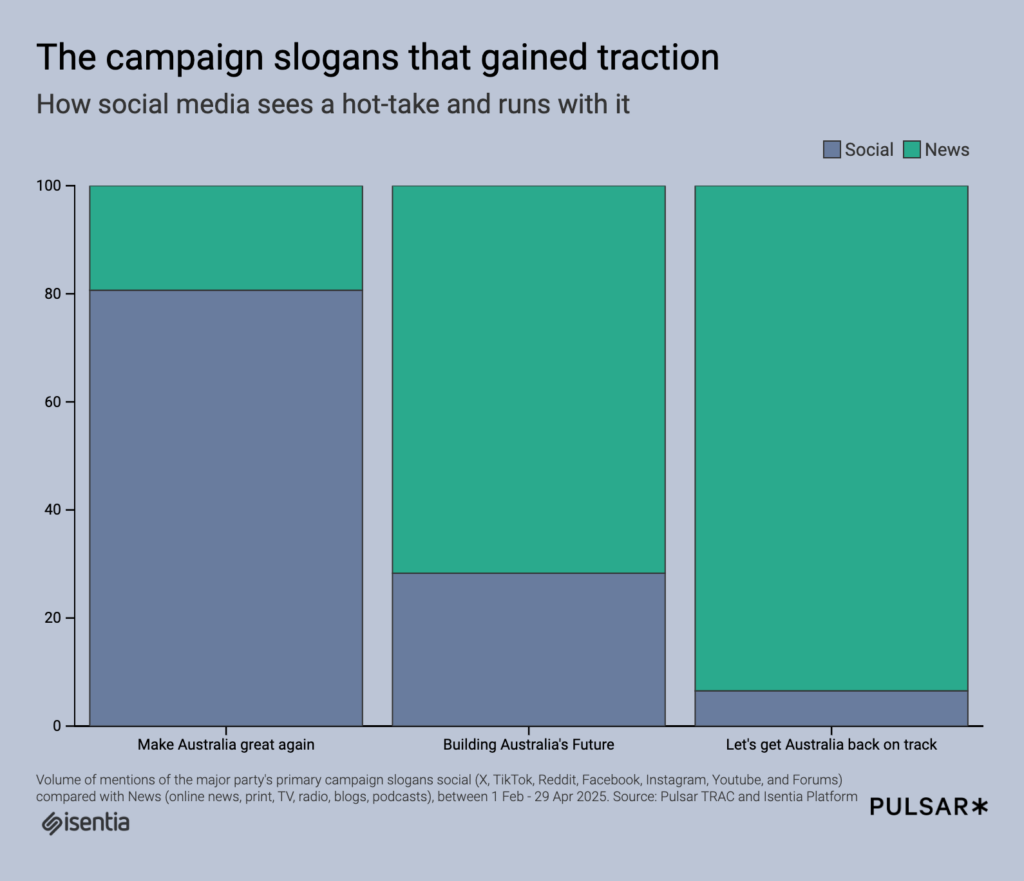
Whether leaders spoke about getting Australia back on track, building a better Australia, or even making Australia great again, these slogans signalled clear messages to voters. More often than not, the public expressed a desire to distance Australia from the United States, particularly in defending healthcare and education systems that set Australia apart. Early in the campaign, when a journalist suggested Anthony Albanese’s use of “build back better” echoed Joe Biden’s slogan, the comment was quickly dismissed. Though not officially endorsed, the slogan’s use by Jacinta Price and Clive Palmer quickly eclipsed party lines, fuelling memes and comparisons to US Republicans across social media. This did little to help the Liberals distance their official slogan, ‘Get Australia back on track,’ from US political parallels. As Trump’s influence became a talking point, glimpses of Trump-style messaging were eagerly picked up by news outlets and social media alike, often overshadowing Labor’s campaign messaging and limiting its cut-through.
As the campaign unfolded, it became harder to separate policy from personality or promises from the cultural narratives surrounding them. Media and social media attention did more than reflect public interest. They helped shape it, steering the election conversation toward identity, values, and questions about Australia’s place in a changing world. Whether that influence outweighed policy in swaying voters is still up for debate, but it clearly changed how the campaign was seen, shared, and remembered.
Loren is an experienced marketing professional who translates data and insights using Isentia solutions into trends and research, bringing clients closer to the benefits of audience intelligence. Loren thrives on introducing the groundbreaking ways in which data and insights can help a brand or organisation, enabling them to exceed their strategic objectives and goals.
Get in touch or request a demo.